How to choose a large format 3d printer
How to choose a large format 3d printer for big 3d printing application?
Large format 3D printers is one of the fastest-growing sectors of the 3D printing market. While some might think large format 3D printers are inaccessible—only a few years ago, prices would start around $100,000—the truth is that today’s large format 3D printing options are much more accessible.
As the options for large format 3D printers are constantly expanding, how can businesses choose the right one?
This buyer's guide will explain how to choose the best large format 3D printer that’s right for any price point and application.
What is a Large Format 3D Printer?
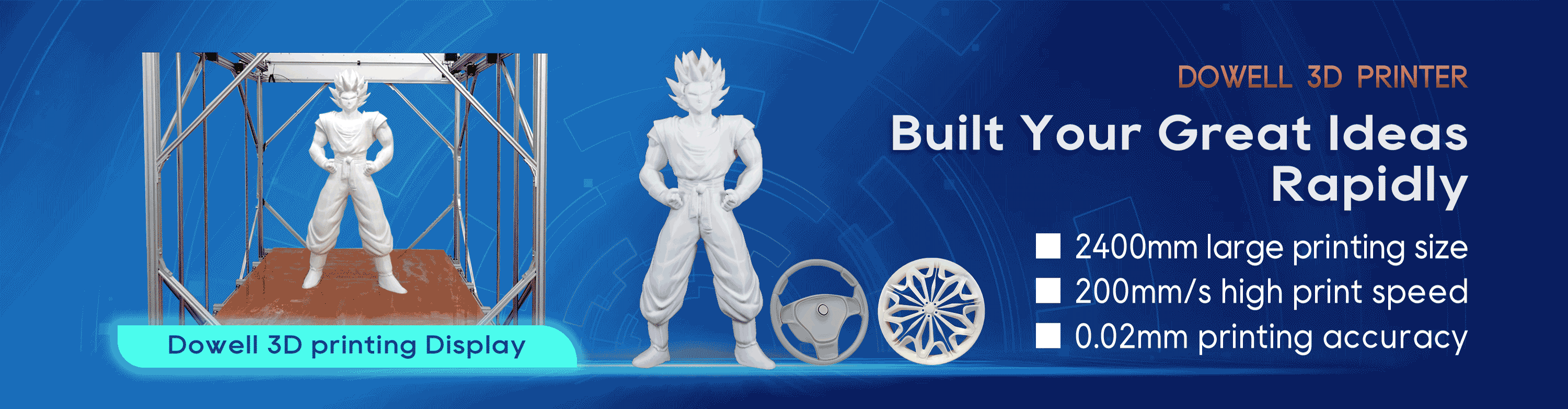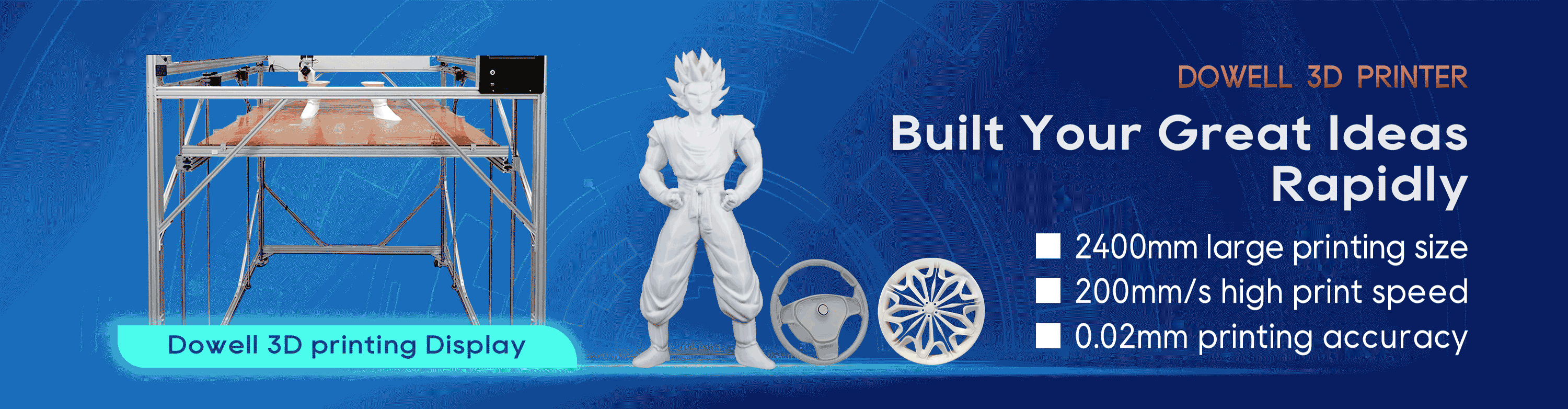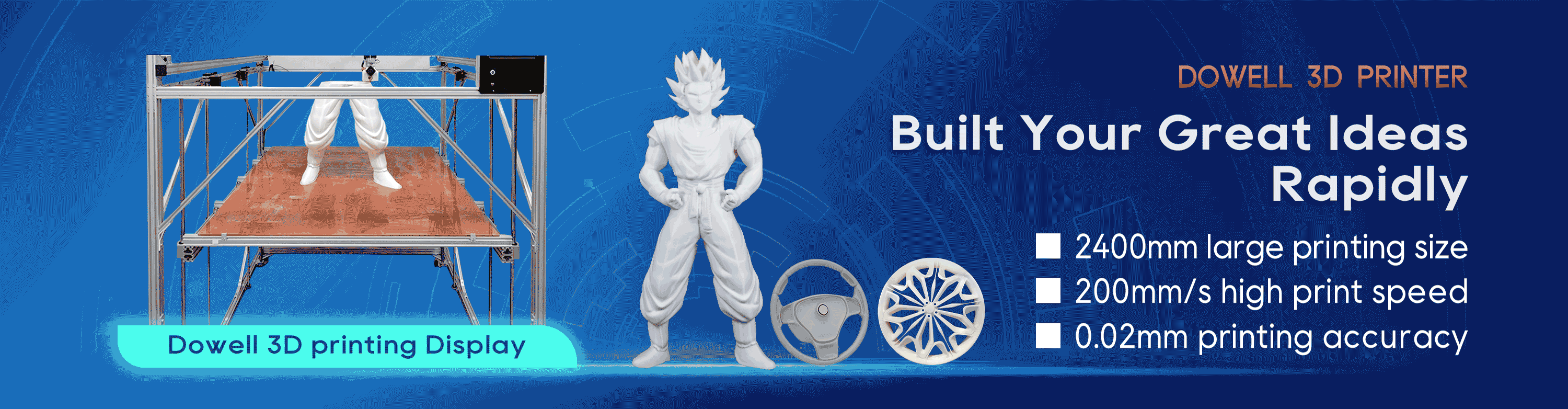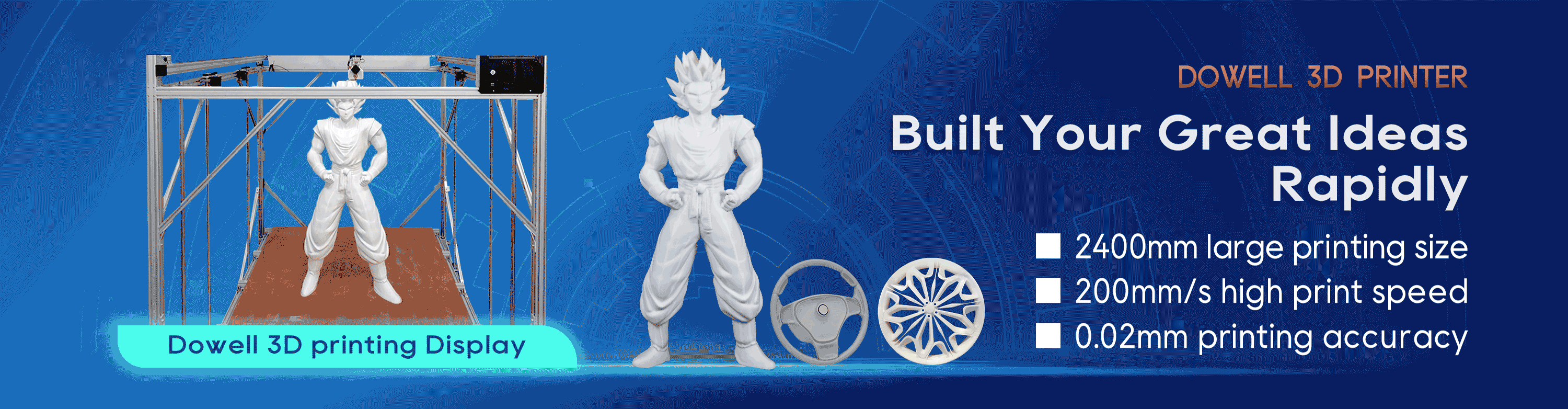
In essence, large format 3D printing today means build volumes beyond the 15-20 cm (5.9-7.9 in) cube dimensions common in desktop FDM 3d printer, Dowell 3d printers offers 3d printer from 40cm to 240cm, covers all the popular 3d printing machine sizes, including 3d printer 1000*1000*1000mm.
Types of Large Format 3D Printers
The three large format 3D printing processes available at accessible prices are the following: fused deposition modeling (FDM), stereolithography (SLA), and selective laser sintering (SLS). Let’s take a closer look at each technology.
In this article, we explore the most common FDM printing technology machines.
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM)
Fused deposition modeling (FDM), also known as fused filament fabrication (FFF), builds parts by melting and extruding thermoplastic filament, which a printer nozzle deposits layer by layer in the build area. FDM is the most widely used form of 3D printing at the consumer level, fueled by the emergence of hobbyist 3D printers.
Mid-range large format FDM printers are available from $4,000 and can typically print objects up to about 30 x 25 x 30 cm in size, while larger systems that can create up to 60 cm tall parts start around $6,000.
All printing equipment provided by dowell3d printer are below market prices and of reliable quality.
FDM Benefits
FDM works with a range of standard thermoplastics 3d printing, such as ABS, PLA, and their various blends. The technique is well suited for basic proof-of-concept models, as well as low-cost prototyping of simple parts, such as parts that might typically be machined.
Disadvantages of FDM
FDM has the lowest resolution and accuracy when compared to SLA or SLS and is not the best option for printing complex designs or parts with intricate features. Higher-quality finishes require labor-intensive and lengthy chemical and mechanical polishing processes. Some large-format FDM 3D printers use soluble supports to mitigate some of these issues and offer a wider range of engineering thermoplastics, but they also come at a steep price. With large parts, FDM printing also tends to be slower than SLA or SLS.